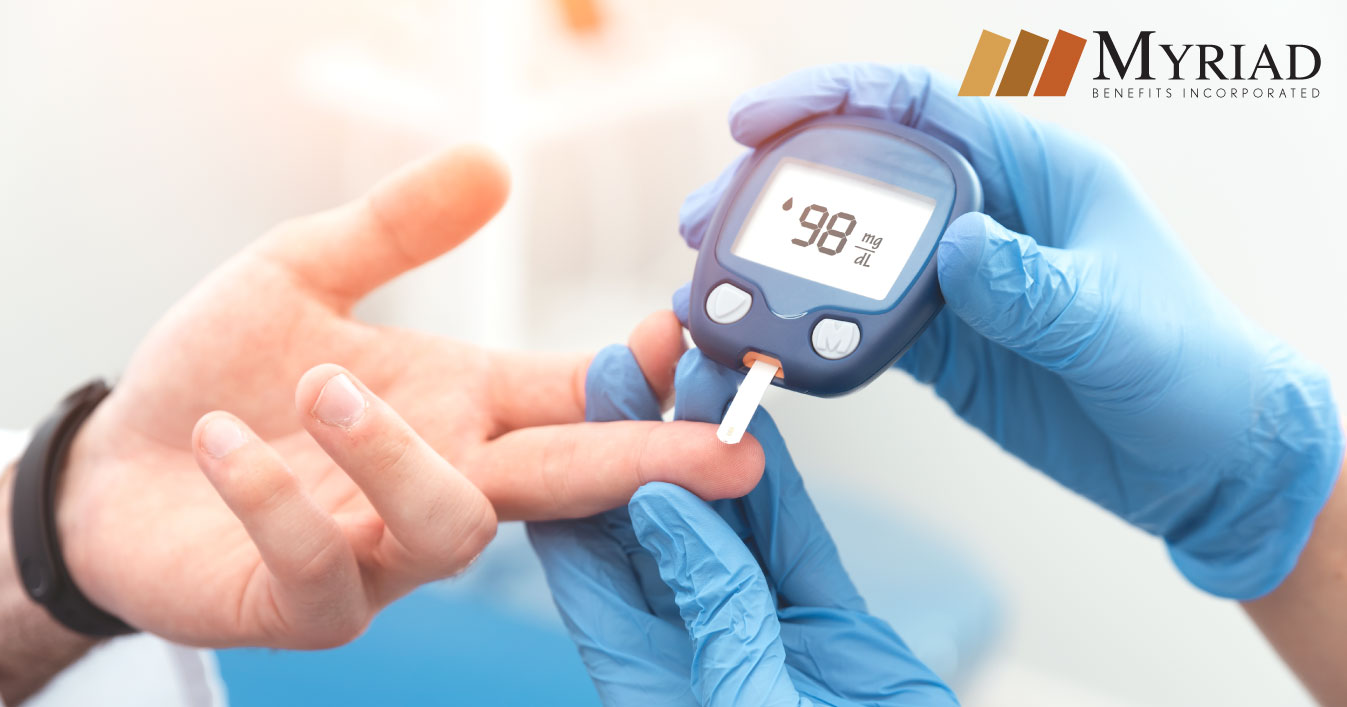
Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the pancreas does not produce insulin or the one that produced by the body cannot use it properly. Insulin is responsible for converting glucose (the sugar we buy from food) into energy. Without insulin, blood sugar levels increase by developing diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, adolescents and young adults. However, it can occur at any age. It is characterized by very little or no insulin production. The most frequent symptoms are constant need to urinate, unusual thirst, extreme hunger, unusual weight loss and extreme fatigue and irritability.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common. In this case the body does not produce enough insulin, or the cells do not use it. You may have any of the symptoms of type 1 diabetes, in addition to blurred vision, cuts / bruises that take time to heal, tingling or numbness in the hands or feet and recurring infections of the skin, gums or bladder.
If you have one or more of the symptoms of type 1 or type 2 diabetes, consult your doctor immediately. Early detection and treatment of symptoms may decrease the possibility of developing diabetes complications.
1.
Do physical activity 30 minutes a day, at least 5 days a week.
2.
Maintain a healthy weight.
3.
Increase the consumption of fiber and fresh vegetables in your daily diet.
4.
Eliminate tobacco and alcohol.
5.
Check your blood sugar levels 3-4 times a day, or as recommended by your doctor.
6.
Visit your doctor regularly.
It is in your hands to control diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. If you have any questions, ask your doctor.
Por: Tania Mangual-Monzón, MS
References:
Centros para el Control y la Prevención de Enfermedades
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/spanish/living/index.html
American Diabetes Association